| |
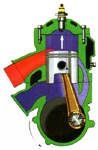
Compression |
 |
| |
The
mixture that occupies the cylinder is compressed by the piston as it
ascends, once it has passed the exhaust port. |
| |
Entry to
the crankcase |
|
As the piston
rises and the volume of the space beneath it increases, fresh fuel
mixture is drawn into the crankcase thought the inlet port which has
been uncovered by the piston skirt. |
| |
|
|
| |
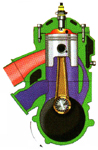
Combustion |
|
| |
As
the piston approaches the top of its travel, the spark plug ignites the
compressed charge which expands rapidly to push the piston down
again. |
| |
Completition
of Induction |
|
Crankcase filling
is now complete and the fresh mixture is ready for transfer to the
cylinder once expansion is complete. |
| |
|
|
| |
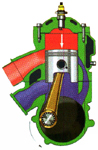
Expansion |
|
| |
As
the piston descends, the energy in the burnt charge is dissipated, power
generation continuing until the piston uncovers the exhaust port ready
to begin the next phase of the cycle. |
| |
Precompression |
|
The decent of the
piston in the cylinder reduces the effective volume of the crankcase and
precom-presses the fresh charge within it to facilitate to the
cylinder. |
| |
|
|
| |
Exhaust |

|
| |
With
the exhaust port uncovered, the burnt gasses are expelled from the
cylinder, helped on their way by a fresh charge entering thought the transfer
port. |
| |
Transfer |
|
With the piston
near the bottom of its stroke it uncovers the transfer port and the pre
compressed charge is forced thought the port from the crankcase into the
cylinder ready for compression. |


